


How Interest Rates are Determined: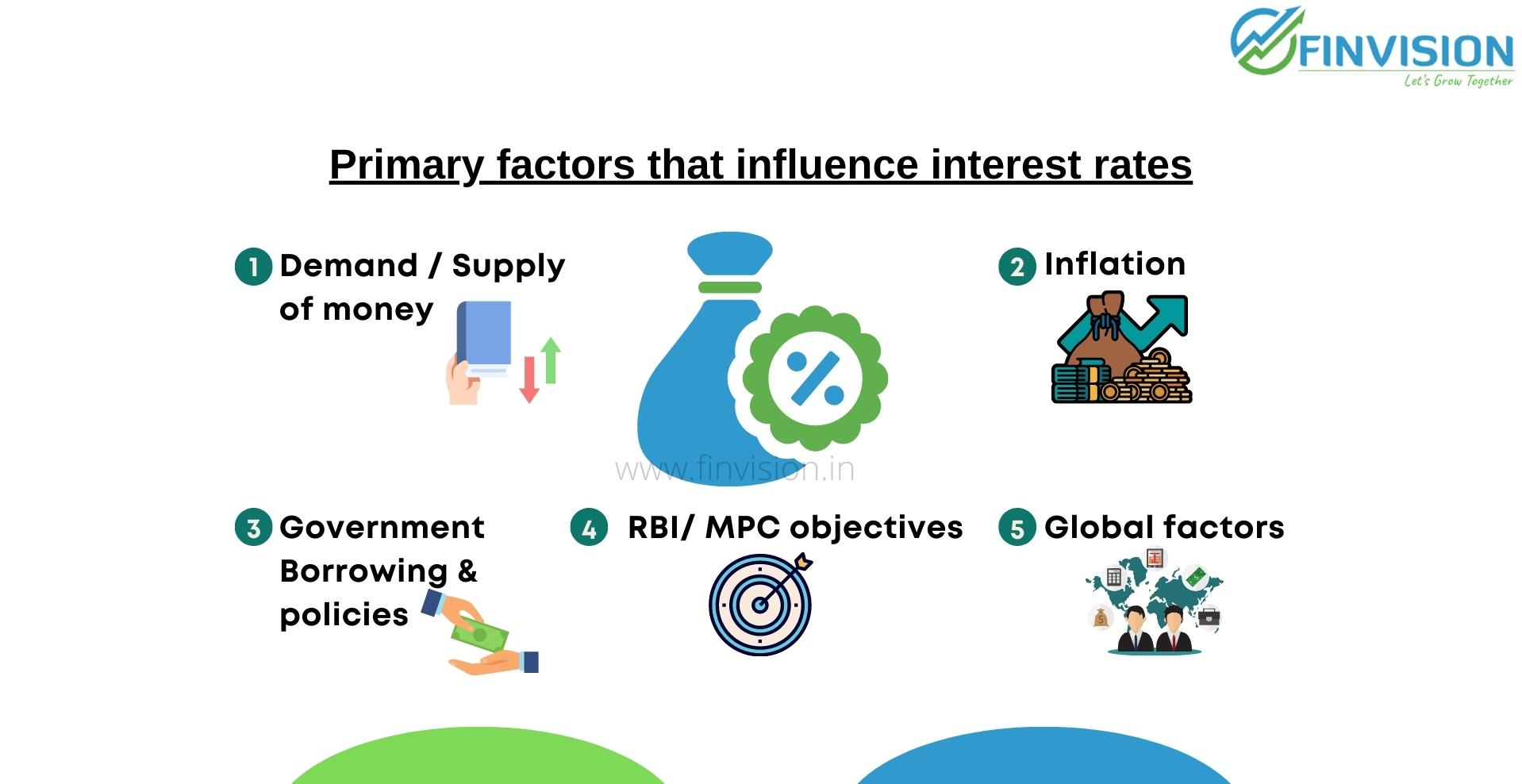

1. Supply and demand of credit:
– Growing economy has a high demand of money (credit)
– Corporates borrow for expansion
– Individuals borrow for house, car, household items, etc.
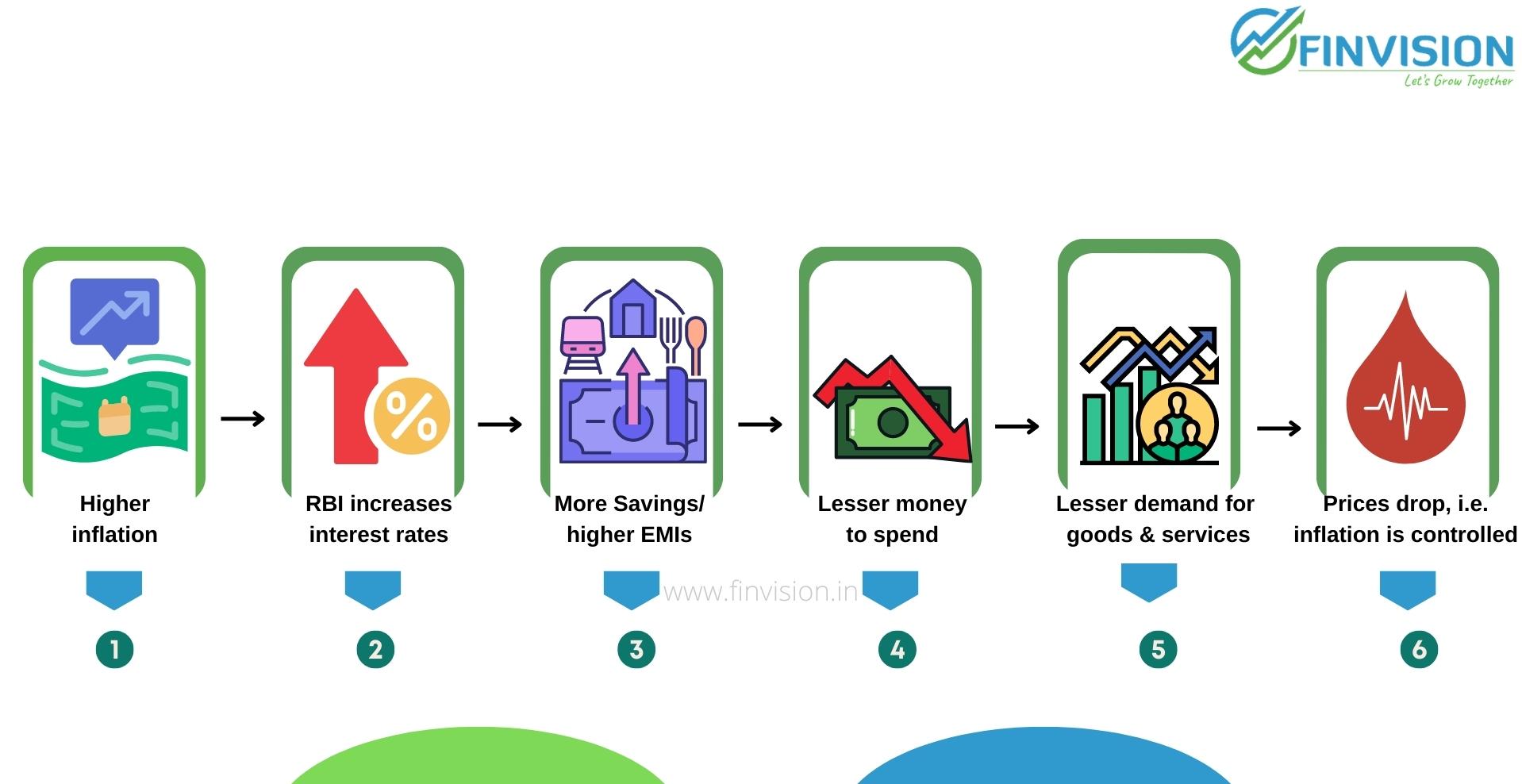
2 Inflation:
– High inflation results in higher interest rates. This occurs because lenders will demand higher interest rates as compensation for the decrease in purchasing power of the money they are paid in the future. Also, as excess liquidity in circulation is absorbed back
– Lower inflation leads to lower interest rates, and the focus shifts to growth
3. Government Borrowings and policies:
– To fund a fiscal deficit, the government resorts to borrowing
– The quantum of this borrowing influences the demand for money and impacts interest rates
– When the government buys more securities, banks are injected with more money than they can use for lending, and the interest rates decrease. Opposite happens when the government sells securities thus forcing a rise in interest rates
Interest keeps the economy moving by encouraging people to borrow, to lend, and to spend
4. RBI/ MPC Objectives:
– The objectives of the MPC are to spur economic growth and to contain inflation
– Low interest rates lead to higher growth
– Major tools with RBI are Repo/ Reverse repo rates and Standard Deposit Facility
5. Global Factors: Interest rates in India generally tend to align with global trends in interest rates and economic environment. For example, Global Financial Crises of 2008 and breakout of Covid in 2020 lead to reduction in interest rates world over.
In this blog we have shared few basics on interest rates. Want to know on the past trend of interest rates, how interest rates affect your market investments, and which businesses, sectors and stocks benefit from increasing interest rate/inflationary trends in economy? Do subscribe to our newsletter and follow our LinkedIn page and contact #Team Finvision for any of your Retirement planning, Investment, Insurance and tax optimising needs.











